The 10 Coolest New AWS Tools Of 2021 (So Far)
CRN highlights some of the top new Amazon Web Services products and services to watch this year.

A new EC2 instance powered by Graviton2 processors, a fintech offering and a service making it easier to run containers on the AWS cloud are among the top Amazon Web Services releases standing out this year.
The Amazon EC2 X2gd Instances are next-generation, memory-optimized instances. Amazon FinSpace is the fintech play, and AWS App runner is the fully managed container application service.
Other AWS products and services that have become generally available in the last approximately six months include a cost anomaly detection tool and a new machine learning-powered service that makes it easier to improve applications’ operational performance and availability.
Here’s a closer look at those offerings and several others that CRN has pegged as 10 of the coolest new AWS tools of 2021 so far.
For more of the biggest startups, products and news stories of 2021 so far, click here .
See the newest entry: The 10 Coolest New AWS Tools Of 2022 (So Far)

Amazon EC2 X2gd Instances
Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute (Amazon EC2) X2gd instances are AWS’ next generation of memory-optimized instances powered by AWS-designed, Arm-based Graviton2 processors and built on the AWS Nitro System.
Announced in March, the EC2 X2gd instances deliver up to 55 percent better price performance for memory-intensive workloads than current-generation x86-based X1 instances, according to the cloud provider, and offer the lowest cost per GiB of memory in Amazon EC2. They also offer increased memory per vCPU compared to AWS’ other Graviton2-based instances, including twice as much memory per vCPU as the memory-optimized R6g instances.
The EC2 X2gd instances support memory-intensive workloads including in-memory databases such as Redis and Memcached, relational databases such as MySQL and PostGreSQL, data warehousing applications such as Amazon Redshift and electronic design automation, according to AWS. Customers also can bundle more memory-intensive containerized applications on a single instance to lower their total cost of ownership.
The new EC2 instances are available in eight sizes and in bare metal form.

AWS Cost Anomaly Detection
AWS Cost Anomaly Detection provides automated cost anomaly detection and root cause analysis to help customers monitor their AWS cloud spending and reduce the risk of billing surprises.
It uses a multi-layered machine learning model that learns customers’ unique, historic AWS spending patterns to detect one-time cost spikes and/or continuous cost increases. Customers don’t have to define anomaly thresholds, as AWS’ learning models automatically will determine them. They can view every anomaly detected in a detection history tab, and AWS sends anomaly detection reports with root-cause analysis that includes the account ID, the service that’s responsible for the anomaly, the severity, duration, etc.
Customers can create their own contextualized cost monitors to define the spend segments they want to evaluate and receive alerts with just three simple steps, according to AWS.The four types of cost monitors are individual AWS services, linked/member accounts, cost allocation tags and cost categories. Customers can customize the alert threshold and frequency, along with alert recipients.
As customers evaluate the anomalies detected, they can submit assessments that will further train the machine learning models so they are tailored to their specific spend patterns.
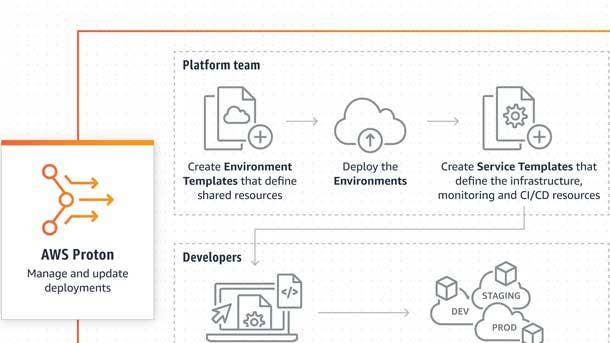
AWS Proton
AWS Proton is a fully managed delivery service that creates and manages standardized infrastructure and deployment tooling for developers and their serverless and container-based applications. It became generally available in June.
AWS Proton is designed for users to more easily provision, deploy and monitor microservices that are the foundation of modern container and serverless apps. It provides management tools, governance and visibility required for consistent standards and best practices for managing deployments, while also helping increase developer productivity, according to AWS.
AWS Proton has a two-pronged automation framework: Platform operators can use infrastructure as code to create versioned service templates that define and configure what’s needed to provision, deploy and monitor a service, and developers then can choose published stacks to rapidly build applications, knowing they are working with up-to-date, validated tools and infrastructure.
Two new features were added since AWS Proton’s launch in preview last fall. It now supports multi-account infrastructures, allowing platform operators to use it to help securely configure and manage their architectures across multiple AWS accounts. It also includes support for identity and access management condition context keys in AWS Proton APIs, allowing platform operators to designate which developers can create services based on template characteristics.
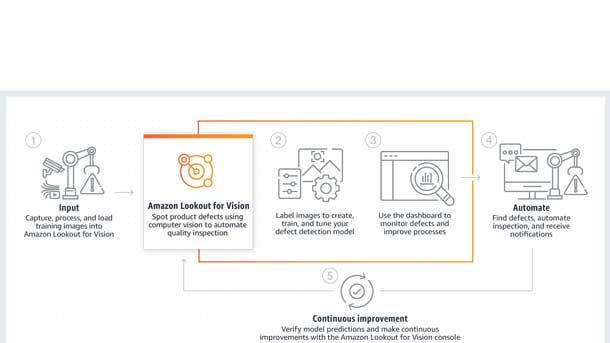
Amazon Lookout for Vision
Amazon Lookout for Vision, a machine learning service that identifies defects and anomalies in visual representations, was launched into general availability in February.
It uses AWS-trained computer vision models to analyze images and video streams to find flaws and anomalies in manufactured products or production processes, damage to vehicles or structures, and defects in silicon wafers or any physical item where quality is important, such as a missing capacitor on printed circuit boards, according to AWS.
Amazon Lookout for Vision uses a machine learning technique called “few-shot learning” to train a model for a customer using as few as 30 baseline images. It can process thousands of images an hour with no machine learning experience required on the part of the user.
The offering analyses the data and then reports images that differ from the baseline through the service dashboard or a “DetectAnomalies” real-time API. The service is advanced enough to maintain high accuracy with variances in camera angle, poses and lighting arising from changes in work environments, according to AWS, and it can use feedback to retrain the underlying model so it continuously improves.
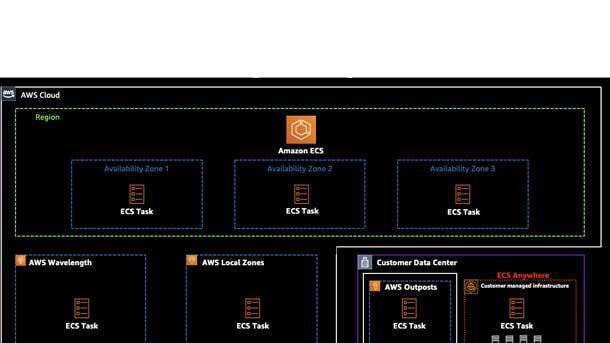
Amazon ECS Anywhere
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a cloud-based, fully managed container orchestration service that became available to all AWS customers in 2015. It now has a new extension that allows customers to deploy native Amazon ECS tasks in any environment: Amazon ECS Anywhere, which became generally available in May.
Amazon ECS Anywhere enables users to easily run and manage container-based applications on premises, including on virtual machines, bare metal servers and other customer-managed infrastructure. Customers get the same AWS-style APIs and cluster configuration management pieces on premises as in in the cloud. Amazon ECS Anywhere precludes them from having to run or maintain their own container orchestrators on-premises.
Benefits include reduced costs and complexity when running container workloads such as data processing at edge locations on a customer’s hardware with reduced latency, and in the cloud using one standardized container orchestrator, according to AWS.
AWS App Runner
April saw the announcement of AWS App Runner as the simplest way for developers to quickly build and run their containerized web applications in AWS – without having prior container or cloud infrastructure experience.
The fully managed, container-native service is designed to make it easier for users to deploy from source code or a container image directly to a scalable and secure web application. Customers aren’t required to configure orchestrators, set up build pipelines, optimize load balancers or rotate transport layer security certificates.
App Runner connects directly to the customer’s code or image repository, and provides a high-performing, automatic integration-and-delivery pipeline with scalability and security, according to AWS.
Developers can use App Runner to simplify the deployment of a new version of code or an image repository.
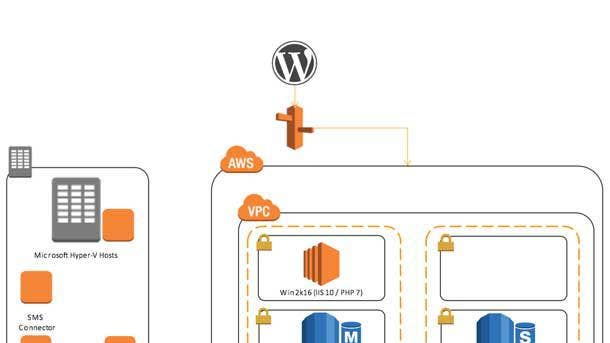
AWS Application Migration Service
Introduced in May, the AWS Application Migration Service (AWS MGN) is a highly automated lift-and-shift solution that simplifies, expedites and reduces the cost of migrating on-premises to AWS.
The agentless service allows users to move applications to AWS without having to make any changes to the applications, their architecture or the migrated servers. It can be used to migrate any application from any source infrastructure that runs supported operating systems, including enterprise applications such as SAP CRM, Oracle E-Business Suite and Microsoft SharePoint, and commercial databases. It continuously replicates a user’s source servers without interfering with the normal operation of the servers, enables non-disruptive testing prior to cutover and allows for cutover windows measured in minutes.
AWS now recommends AWS MGN as the primary migration service for lift-and-shift migrations to AWS, and it’s encouraging customers using CloudEndure Migration or AWS Server Migration Service (AWS SMS) to switch to it for future migrations. AWS MGN minimizes time-intensive, error-prone manual processes by automatically replicating entire servers and converting source servers from physical, virtual or cloud infrastructure to run natively on AWS, according to the cloud provider.
AWS MGN is based on the CloudEndure Migration’s technology and has similar capabilities, but it’s available on the AWS Management Console, enabling seamless integration with other AWS services, such as AWS CloudTrail, Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Identity and Access Management.
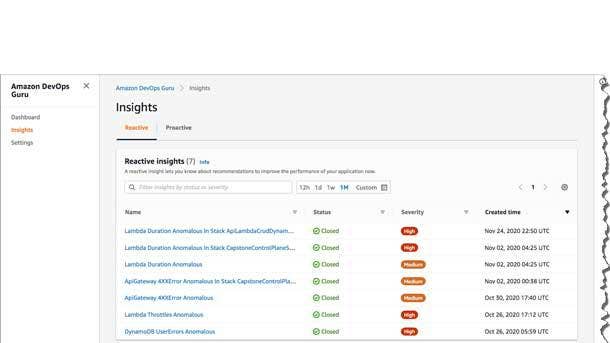
Amazon DevOps Guru
Amazon DevOps Guru identifies potential operational issues to help developers and operators improve the performance and availability of their operational applications before they impact customers.
The new service became generally available in May. It uses machine learning to analyze operational data and application metrics and events to identify behaviors that deviate from normal operating patterns and could cause potential outages or service disruptions, such as potential issues with missing or misconfigured alarms, resources that are approaching resource limits, code changes that could cause outages, under-provisioned capacity, over-utilization of databases or memory leaks.
When DevOps Guru detects an operational issue or risk, users are notified via an Amazon Simple Notification Service notification, a CloudWatch event or third-party tools such as Slack. DevOps Guru provides context on the resources involved and related events and provides specific recommended remediation steps. Developers can use those recommendations to reduce time to resolution with no manual setup or machine learning expertise required.

Amazon FinSpace
Amazon FinSpace is a data management and analytics service designed to make it easier to store, catalog and prepare financial industry data at scale. Purpose-built for the financial service industry, the fully managed service removes the heavy lifting of building and maintaining a data management system for financial analytics, reducing the time for financial industry customers to locate and access all types of financial data for analysis
Amazon FinSpace automates the process for finding data, preparing it for analysis, storing and organizing it using industry and internal data classification conventions. Data can be collected in a secure data management application and catalogued by applicable business concepts such as asset class, risk classification or geographic region. Analysts can connect to the Amazon FinSpace web interface to search for data using familiar business terms such as “S&P 500,” “CAC 40” or “private equity funds in euros,” for example.
AWS has a built-in library of more than 100 specialized functions for time series data — think time bars and Bollinger Bands — that analysts can use to prepare their chosen data sets. They also can integrate their own functions. Amazon FinSpace provides a framework to manage and audit data access, and it generates compliance and audit reports.

Amazon S3 Object Lambda
AWS introduced Amazon S3 Object Lambda in Marchto give customers the ability to use their code to process data as it’s being retrieved from Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), making it easier to share and convert data across multiple applications.
Amazon S3 Object Lambda works with their existing applications and uses AWS Lambda functions to automatically process and transform the data as it is being retrieved from S3, without having to change application codes. The Lambda function is invoked in line with a standard S3 GET request. (AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets users run code without thinking about servers or clusters).
Amazon S3 Object Lambda allows users to easily present multiple views from the same dataset and update the Lambda functions to modify the views at any time.