Google I/O: 8 Huge AI, Workspace, Bard, Google Cloud Launches
From the launch of Duet AI for both Google Workspace and Google Cloud, to huge improvements to Vertex AI and Google Bard, CRN breaks down the eight most important launches at Google I/O 2023.

Google is diving deeper into artificial intelligence and generative AI than ever before with the launch of a slew of new AI capabilities and software for its most popular offerings including Google Workspace and Google Cloud.
At Google I/O 2023, CEO Sundar Pichai (pictured) spoke extensively about his company’s goal of becoming the market leader in AI and generative AI as the company unveiled new products and capabilities.
“Seven years into our journey as an AI-first company, we’re at an exciting inflection point,” said Sundar Pichai during his keynote speech at Google I/O. “We have an opportunity to make AI even more helpful for people, for businesses, for communities, for everyone. We’ve been applying AI to make our products radically more helpful for a while. With generative AI, we’re taking the next step.”
[Related: Google’s Top 5 Execs Compensated $350 Million In 2022: Here’s Who They Are]
The $280 billion Mountain View, Calif.-based technology giant is investing heavily in injecting AI across its entire massive portfolio of cloud computing, collaboration and consumer offerings. Additionally, Google is providing developers new tools and capabilities to help them innovate.
“The shift with AI is as big as they come and that’s why it’s so important that we make AI helpful for everyone,” said Pichai. “No one company can do this alone. Our developer community will be key to unlocking the enormous opportunities ahead. We look forward to working together and building together.”
From the launch of Duet AI for both Google Workspace and Google Cloud, to significant improvements to Vertex AI and Google Bard, CRN breaks down the eight most important news and launches at Google I/O 2023. These include:
*Duet AI For Google Workspace
*PaLM 2
*New Bard Capabilities
*Vertex AI New Foundation Models
*Google A3 Supercomputers With Nvidia H100 GPUs
*Vertex AI Embedded APIs
*Duet AI For Google Cloud
*Vertex AI RLHF
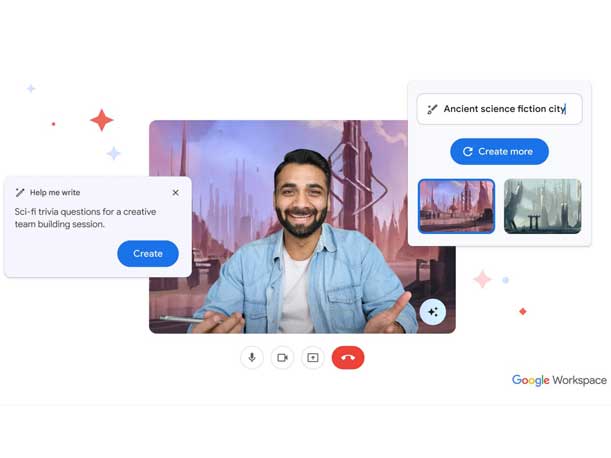
Duet AI For Google Workspace
One of the biggest launches at Google I/O this week is Duet AI For Google Workspace, which brings together all of Google’s powerful generative AI features and lets users collaborate with AI so they can get more done every day.
Google is bringing generative AI capabilities to Gmail on mobile to help users create content and write on the go.
Within Google Slides, the company is embedding generative AI into Slides so users can easily create unique visuals with a few words.
For Sheets, Google’s new generative AI helps users analyze and act on data in Sheets, with automated data classification and the creation of custom tables.
Within Meet, Google’s new AI features enables users to express themselves better during video calls with custom backgrounds in Meet.
Lastly, Google is integrating smart canvas capabilities, such as smart chips, into the new assisted writing experience inside Google Docs.
“These features help you write, help you organize, help you visualize, help you accelerate workflows, have richer meetings and much more,” said Aparna Pappu, general manager and vice president of Google Workspace, in a blog post.

PaLM 2: Google’s Next Generation Language Model
Google unveiled a new version of its large language model PaLM 2.
PaLM 2 models deliver top-notch foundational capabilities across a wide range of sizes called: Gecko, Otter, Bison, and Unicorn. For example, Gecko is lightweight so that it can work on mobile devices and is fast enough for great interactive applications on-device, even when offline.
“PaLM 2 models are stronger in logic and reasoning thanks to broad training on scientific and mathematical topics,” said Google’s CEO Pichai during the event. “It’s also trained on multilingual text—spanning more than 100 languages—so it understands and generates nuanced results.”
PaLM 2’s wide-ranging dataset includes scientific papers and web pages that contain mathematical expressions. As a result, it demonstrates improved capabilities in logic, common sense reasoning, and mathematics.
On the coding front, PaLM 2 was pre-trained on a large quantity of publicly available source code datasets. This means that it excels at popular programming languages like Python and JavaScript, but can also generate specialized code in languages like Prolog, Fortran and Verilog.

New Bard Capabilities
At Google I/O, the company introduced new updates to Bard, including moving it to Google’s new PaLM 2 large language model.
Bard will soon become more visual both in its responses and to user prompts.
“You’ll be able to ask it things like, “What are some must-see sights in New Orleans?” — and in addition to text, you’ll get a helpful response along with rich visuals to give you a much better sense of what you’re exploring,” said Sissie Hsiao, vice president and general manager for Google Bard and Assistant in a blog post.
Users will also be able to include images, alongside text, in their own prompts—allowing users to boost creativity in new ways. To make this happen, Google brought the power of Goolge Lens into Bard.
Google is also launching new coding upgrades and export features. Bard is on track to support 40 languages in the near future. Additionally, Google opened Bard up to over 180 new counties and territories on a global basis.

Duet AI for Google Cloud
Google is also launching Duet AI for Google Cloud, which is a new AI-powered collaborator to help cloud users of all skill levels solve their everyday work challenges.
Duet AI serves as an expert pair programmer and assists cloud users with contextual code completion, offering suggestions tuned to a customer’s code base, generating entire functions in real time, and assisting with code reviews and inspections.
Duet AI for Google Cloud will fundamentally transform the way cloud users of all skill sets build new experiences and is embedded across Google Cloud interfaces—within the integrated development environment (IDE), Google Cloud Console, and even chat.
“With Duet AI, we’re on a mission to deliver a new cloud experience that’s personalized and intent-driven, and can deeply understand your environment to assist you in building secure, scalable applications, while providing expert guidance,” said Michael Weingartner, vice president and general manager of Google’s Cloud Application Ecosystem in a blog post.
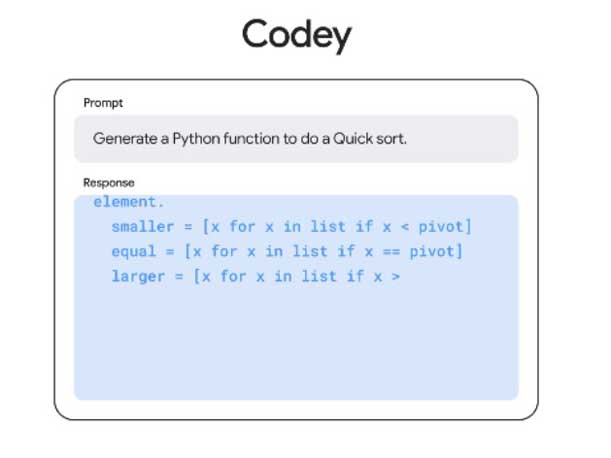
Vertex AI New Foundation Models
Google unveiled three new foundation models available in Vertex AI, where they can be accessed via API, tuned through a simple UI in Generative AI Studio, or deployed to a data science notebook.
These new foundation models are: Codey, Imagen and Chirp.
Codey is Google’s new text-to-code foundation model. It can be embedded in an SDK or application to help improve developer velocity with code generation and code completion, and to improve code quality. Codey accelerates software development with real-time code completion and generation, customizable to a customer’s own codebase.
Imagen is Google’s text-to-image foundation model, which lets organizations generate and customize studio-grade images at scale for any business need. Imagen lets customers generate and edit high-quality images for any business need.
Chirp is the company’s new speech-to-text foundation model. It aims at helping organizations more deeply and inclusively engage with their customers in their native languages with captioning and voice assistance. Chirp helps organizations engage with customers and constituents more inclusively in their native languages.

Vertex AI New RLHF
New Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is extending Vertex AI’s tuning and prompt design capabilities by letting organizations incorporate human feedback to customize and improve model performance.
Google said Vertex AI is the first end-to-end machine learning platform among the cloud hyperscalers to offer RLHF as a managed service offering, helping organizations to cost-efficiently maintain model performance over time and deploy safer and more useful models to production.
This tuning feature Google customers incorporate human feedback to train a reward model that can be used to finetune foundation models. This can be useful in industries where accuracy or customer satisfaction is critical, as it ultimately leads to higher customer satisfaction and engagement. It also lets people more accurately review the model responses for bias, toxic content, or other dimensions, teaching the model to avoid inappropriate outputs.

Google A3 Supercomputers With Nvidia H100 GPUs
Google Cloud is expanding its compute portfolio with the private preview launch of the next-generation A3 GPU supercomputer. The A3 VMs combine Nvidia H100 Tensor Core GPUs with Google’s leading networking advancements to serve customers of all sizes.
The move expands Google’s compute options for machine learnings use cases such as large language models (LLMs), generative AI, and diffusion models.
A3 is the first GPU instance to use Google’s custom-designed 200 Gbps IPUs, with GPU-to-GPU data transfers bypassing the CPU host and flowing over separate interfaces from other VM networks and data traffic.
Google Compute Engine A3 supercomputers are purpose-built to train and serve the most demanding AI models that power today’s generative AI and LLMs innovation.
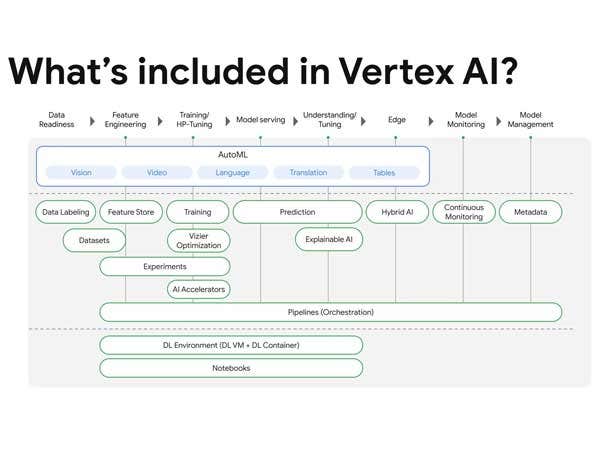
Vertex AI Embedded APIs
Google has embedded APIs for text and images into Vertex AI to help developers build recommendation engines, classifiers, question-answering systems, and other sophisticated applications based on semantic understanding of text or images.
Embeddings convert text and image data into multi-dimensional numerical vectors that map semantic relationships can be processed by large models and are particularly useful for longer inputs, such as texts with thousands of tokens, according to Google.
The new capabilities enable developers to create more compelling apps and user experiences by building powerful semantic search and text classification functionality, creating Q&A chatbots based on an organization’s data, and improving clustering, anomaly detection and sentiment analysis.